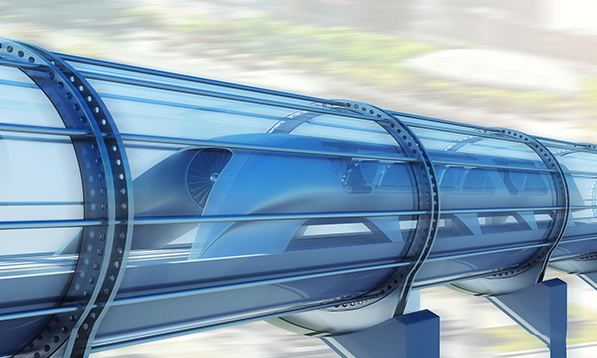
A FUTURISTIC TRANSPORTATION
Humankind has witnessed significant progress since the birth of the human race till today. In this modern era of technological advancement, where technologies have evolved to revolutionize the life of an ordinary man, the modes of transportation haven’t seen significant progress in past decades. Hyperloop is considered to be a transport for a sustainable future.
What is Hyperloop?
Hyperloop is a high-speed transportation system for passenger and freight transport through partial vacuum tubes. It is described as a sealed tube or system of tubes having low pressure with passengers sitting in pods travelling at airline speeds almost without any air resistance or friction. It mainly employs three components- a tube, pod and terminal. Pods travel through evacuated tubes using electric propulsion, air skies and magnetic levitation.
HISTORY
The roots of the Hyperloop can be traced back to 1799 when George Medhurst proposed the idea of moving goods through cast iron pipes using pressurized air. Later for the first time, Isambard Kingdom Brunel’s atmospheric railway ran between Exeter and Plymouth in the UK from 1847 to 1848. The carriages were moved using pressurized air extracted from pipes that ran between the rails by pumping stations. A piston contained within the pipe was connected to the train, which pulled it forward.
Fig 1 : Isambard Kingdom Brunel’s atmospheric railway
Tesla and Spaced founder, Elon Musk introduced the modern idea of Hyperloop with his ‘Hyperloop alpha’ paper in 2013. In his paper, Musk envisioned a super-fast transportation system that is safer, affordable, weatherproof and energy-efficient.
His initial plan comprised of exploring potential route between Los Angeles and San Francisco to reduce four hour train travel to just 30 minutes. The estimated budget was six billion dollars, but his idea never came into existence. Musk “open-sourced” the idea of hyperloop for future experimentation and actively encouraged others to develop the technology without his involvement.
How does it work?
The basic idea behind Musk’s model is that a passenger pod travels through low-pressure tubes. A vacuum pump removes most of the air from the tubes to eliminate friction and air resistance. The operating pressure of 100 pascals is maintained, which reduces the drag force of the air by 1,000 times, and the energy consumption is less compared to traditional modes of transports. Compressor fans are installed to circulate the air around the pod to create an air cushion so that it floats above the tube’s surface, thereby minimizing friction. According to Musk, Hyperloop would be powered by solar panels fitted over tubes.
Fig 2 : Passenger pod using air cushion technology.
Another version of Hyperloop uses magnetic levitation (Mag-lev), a technology already used in monorails. It uses two sets of magnets, one to repel the tracks and lift them upwards and another to keep them floating along the tracks with considerable speeds and minimal friction. It uses a linear electric motor to accelerate and decelerate the pod. Vacuum sealed tubes along with Mag-lev ensures that the pod experiences little to no resistance. Air pressure inside the tubes is equivalent to flying 200000 ft above sea level, enabling pods to travel at maximum speeds of 750 miles/hour.
Current Developments
Recent developments in Hyperloop have led fully-fledged companies like HTT (Hyperloop transportation technologies), Virgin Hyperloop One, Transport and others to make significant strides in bringing Hyperloop into reality. In 2018, HTT constructed a full-scale test track in France. However, Virgin Hyperloop One is considered to be the front runner among the current standings.
Virgin Hyperloop One was first established in the year 2014. They are already on their way to bringing the hyperloop into operation. In 2017, the company conducted several test runs focusing on individual aspects of the system at its test site in Las Vegas, Nevada. Following its successful test trail, a commercial vehicle design was launched recently. The company signed a deal with Dubai’s Road and transport authority to conduct feasibility studies to link Abu Dhabi to Dubai that would reduce a 2-hour road journey to 12 minutes of travel. Also, in February 18, an ‘intent agreement’ was signed with Government of Maharashtra to build a Hyperloop network between Mumbai to Pune.
Fig 3 : Virgin Hyperloop One’s XP-1 passenger pod
Virgin Hyperloop One launched a global challenge to find possible routes that are best placed to benefit from Hyperloop technology. Among those, only 10 potential routes located in 5 different countries were selected by a panel of experts to construct the first hyperloop network. The United States alone has 4 routes connecting Chicago-Columbus-Pittsburgh, Miami – Orlando, Dallas – Houston and Cheyenne – Pueblo. The United Kingdom has two routes linking its major cities Glasgow and Edinburgh to London. In India Bangalore – Chennai and Mumbai – Chennai were the two routes among the ten selected.
REFERENCES